HDR (High Dynamic Range) refers to the range of brightness that a camera or image sensor can capture. This technology allows for detailed representation of both very dark and very bright areas simultaneously. In this article, we will delve into the basic concept of HDR, the definition and calculation of dynamic range in CMOS image sensors, and the technical approaches used to achieve HDR.
What is HDR?
HDR stands for “High Dynamic Range,” a technology that expands the range of brightness a camera or image sensor can capture, also known as dynamic range. In traditional SDR (Standard Dynamic Range), scenes with high contrast often result in crushed shadows or blown-out highlights. By employing HDR technology, these issues can be resolved, enabling a more faithful reproduction of details across the entire scene.
The following image illustrates a comparison between SDR and HDR. In SDR, tonal details in shadows and highlights are lost, whereas HDR effectively preserves both, providing a well-balanced representation.
引用元:Sony What’s HDR(https://imagesensor-info.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=83&action=edit)
Dynamic Range in CMOS Image Sensors
The dynamic range of a CMOS image sensor is defined as the ratio between the darkest and brightest signals the sensor can simultaneously capture. Specifically, it is expressed as the ratio of the pixel’s saturation signal level (Ssat) to the dark current noise (Ndark), calculated using the following formula:
$$ DR = 20logfrac{Ssat}{Ndark}[dB] $$
For example, if the saturation signal is 100,000 and the dark noise is 10, the dynamic range is 100 dB. Generally, a dynamic range of 100 dB or higher is considered to have HDR performance.
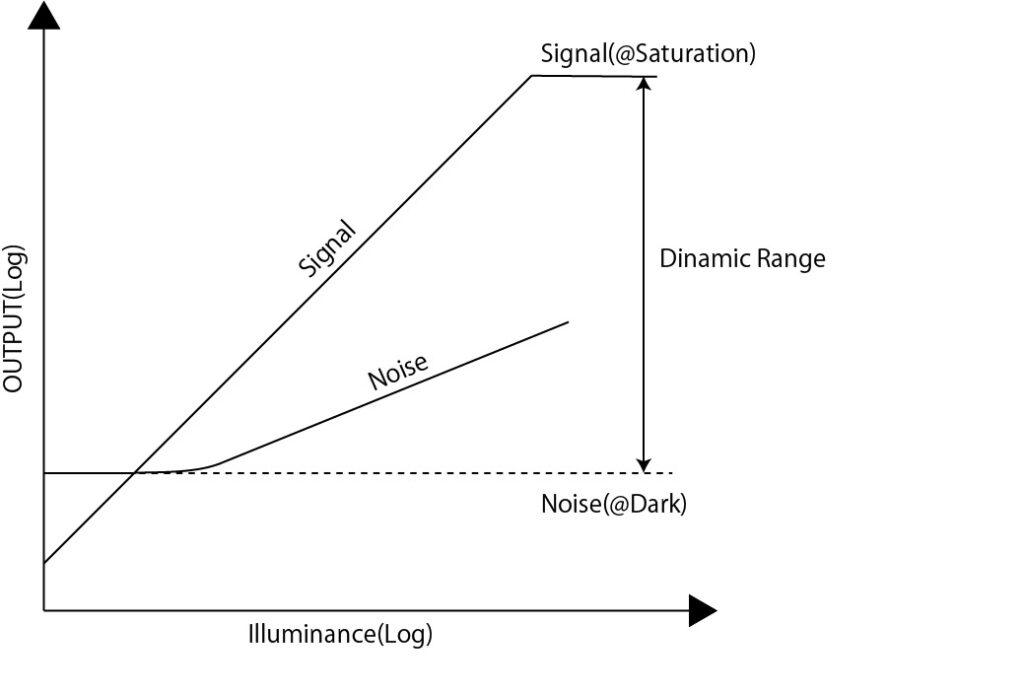
Methods to Expand Dynamic Range
To expand the dynamic range of CMOS image sensors, the following approaches can be considered:
- Increasing Saturation Capacity: By increasing the pixel’s saturation capacity, the maximum number of photons the sensor can capture is increased, enabling better acquisition of highlight details.
- Reducing Noise: Lowering dark current and readout noise improves the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in dark areas, allowing clearer capture of shadow details.
- Multiple Exposure Synthesis: This technique generates an image with a wide dynamic range by combining multiple images taken at different exposure times. It effectively represents details in both bright and dark areas.
These technical approaches enhance the dynamic range capabilities of CMOS image sensors.
Conclusion
HDR (High Dynamic Range) technology enables cameras and image sensors to simultaneously capture details from very dark to very bright areas. The dynamic range of CMOS image sensors is determined by the ratio of pixel saturation capacity to dark current noise. To expand this range, methods such as increasing saturation capacity, reducing noise, and combining multiple exposures are employed. These techniques make it possible to achieve higher-quality images.
Q. What is Dynamic Range?
A. It refers to the range of brightness a sensor can handle.
$$ DR = 20logfrac{Ssat}{Ndark}[dB] $$
represents this relationship.
Q. What is HDR?
A. It stands for High Dynamic Range.
(While not strictly defined, it is often considered HDR if the dynamic range exceeds approximately 100 dB.)
We also provide explanations about image sensors, so please take a look!





コメント